
1. Windows Management. By now, you’ve probably seen that Windows 7 does a lot to make window management easier: you can “dock” a window to the left or right half of the screen by simply dragging it to the edge; similarly, you can drag the window to the top of the screen to maximize it, and double-click the window top / bottom border to maximize it vertically with the same horizontal width. What you might not know is that all these actions are also available with keyboard shortcuts:
i. Win+Left Arrow and Win+Right Arrow dock;
ii. Win+Up Arrow and Win+Down Arrow maximizes and restores / minimizes;
iii. Win+Shift+Up Arrow and Win+Shift+Down Arrow maximizes and restores the vertical size.
This side-by-side docking feature is particularly invaluable on widescreen monitors – it makes the old Windows way of shift-clicking on two items in the taskbar and then using the context menu to arrange them feel really painful.
2. Cut Out The Clutter. Working on a document in a window and want to get rid of all the extraneous background noise? Simply hit Win+Home to minimize all the non-active background windows, keeping the window you’re using in its current position. When you’re ready, simply press Win+Home again to restore the background windows to their original locations. Alternatively (and more fun) is to grab the Window by its top bar and shake it. Do it again to restore the other Windows.
3. It’s a Global Village. If you’ve tried to change your desktop wallpaper, you’ve probably noticed that there’s a set of wallpapers there that match the locale you selected when you installed Windows. (If you picked US, you’ll see beautiful views of Crater Lake in Oregon, the Arches National Park, a beach in Hawai’i, etc.) In fact, there are several sets of themed wallpapers installed based on the language you choose, but the others are in a hidden directory. If you’re feeling in an international mood, simply browse to C:\Windows\Globalization\MCT and you’ll see a series of pictures under the Wallpaper directory for each country. Just double-click on the theme file in the Theme directory to display a rotation through all the pictures for that country. (Note that some countries contain a generic set of placeholder art for now.)
4. Who Stole My Browser? If you feel like Internet Explorer is taking a long time to load your page, it’s worth taking a look at the add-ons you have installed. One of the more helpful little additions in Internet Explorer 8 is instrumentation for add-on initialization, allowing you to quickly see whether you’re sitting around waiting for plug-ins to load. Just click Tools / Manage Add-ons, and then scroll right in the list view to see the load time. On my machine, I noticed that the Research add-on that Office 2007 installs was a particular culprit, and since I never use it, it was simple to disable it from the same dialog box.
5. Rearranging the Furniture. Unless you’ve seen it demonstrated, you may not know that the icons in the new taskbar aren’t fixed in-place. You can reorder them to suit your needs, whether they’re pinned shortcuts or running applications. What’s particularly nice is that once they’re reordered, you can start a new instance of any of the first five icons by pressing Win+1, Win+2, Win+3 etc. What’s less well-known is that you can similarly drag the system tray icons around to rearrange their order, or move them in and out of the hidden icon list. It’s an easy way to customize your system to show the things you want, where you want them.
6. It’s also worth noting in passing that Windows 7 is far better suited to a netbook than any previous operating system: it has a much lighter hard drive and memory footprint than Windows Vista, while also being able to optimize for solid state drives (for example, it switches off disk defragmentation since random read access is as fast as sequential read access, and it handles file deletions differently to minimize wear on the solid state drive).
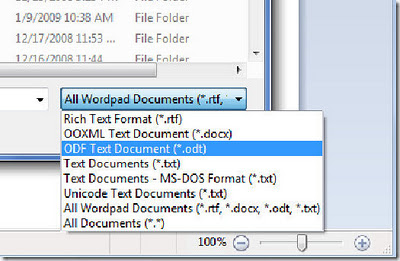
7. Standards Support. Every review of Windows 7 that I’ve seen has noted the revamped WordPad and Paint applets that add an Office-like ribbon to expose their functionality. Few, however, have noticed one small but hopefully appreciated feature: WordPad can now read and write both the Word 2007-compatible Office Open XML file format but also the OpenDocument specification that IBM and Sun have been advocating:
8. Windows Vista-Style Taskbar. I wasn’t initially a fan of the Windows 7 taskbar when it was first introduced in early Windows 7 builds, but as the design was refined in the run up to the beta, I was converted and now actively prefer the new look, particularly when I’ve got lots of windows open simultaneously. For those who really would prefer a look more reminiscent of Windows Vista, the good news is that it’s easy to customize the look of the taskbar to more closely mirror the old version:

To achieve this look, right-click on the taskbar and choose the properties dialog. Select the “small icons” checkbox and under the “taskbar buttons” setting, choose “combine when taskbar is full”. It’s not pixel-perfect in accuracy, but it’s close from a functionality point of view.
9. Peeking at the Desktop. While we’re on the taskbar, it’s worth noting a few subtleties. You’ve probably seen the small rectangle in the bottom right hand corner: this is the feature we call “Aero Peek”, which enables you to see any gadgets or icons you’ve got on your desktop. I wanted to note that there’s a keyboard shortcut that does the same thing – just press Win+Space.
10. Running with Elevated Rights. Want to quickly launch a taskbar-docked application as an administrator? It’s easy – hold down Ctrl+Shift while you click on the icon, and you’ll immediately launch it with full administrative rights (assuming your account has the necessary permissions, of course!)
11. One More of the Same, Please. I’ve seen a few folk caught out by this one. If you’ve already got an application open on your desktop (for example, a command prompt window), and you want to open a second instance of the same application, you don’t have to go back to the start menu. You can simply hold down the Shift key while clicking on the taskbar icon, and it will open a new instance of the application rather than switching to the existing application. For a keyboard-free shortcut, you can middle-click with the third mouse button to do the same thing. (This trick assumes that your application supports multiple running instances, naturally.)
12. Specialized Windows Switching. Another feature that power users will love is the ability to do a kind of “Alt+Tab” switching across windows that belong to just one application. For example, if you’ve got five Outlook message windows open along with ten other windows, you can quickly tab through just the Outlook windows by holding down the Ctrl key while you repeatedly click on the single Outlook icon. This will toggle through each of the five Outlook windows in order, and is way faster than opening Alt+Tab and trying to figure out which of the tiny thumbnail images relates to the specific message you’re trying to find.
13. Walking Through the Taskbar. Another “secret” Windows shortcut: press Win+T to move the focus to the taskbar. Once you’re there, you can use the arrow keys to select a particular window or group and then hit Enter to launch or activate it. As ever, you can cancel out of this mode by hitting the Esc key. I don’t know for sure, but I presume this shortcut was introduced for those with accessibility needs. However, it’s equally valuable to power users – another good reason for all developers to care about ensuring their code is accessible.
 14. The Widescreen Tip. Almost every display sold these days is widescreen, whether you’re buying a notebook computer or a monitor. While it might be great for watching DVDs, when you’re trying to get work done it can sometimes feel like you’re a little squeezed for vertical space.
14. The Widescreen Tip. Almost every display sold these days is widescreen, whether you’re buying a notebook computer or a monitor. While it might be great for watching DVDs, when you’re trying to get work done it can sometimes feel like you’re a little squeezed for vertical space.As a result, the first thing I do when I set up any new computer is to dock the taskbar to the left hand side of the screen. I can understand why we don’t set this by default – can you imagine the complaints from enterprise IT departments who have to retrain all their staff – but there’s no reason why you as a power user should have to suffer from default settings introduced when the average screen resolution was 800x600.
In the past, Windows did an indifferent job of supporting “side dockers” like myself. Sure, you could move the taskbar, but it felt like an afterthought – the gradients would be wrong, the Start menu had a few idiosyncrasies, and you’d feel like something of a second-class citizen. The Windows 7 taskbar feels almost as if it was designed with vertical mode as the default – the icons work well on the side of the screen, shortcuts like the Win+T trick mentioned previously automatically switch from left/right arrows to up/down arrows, and so on. The net effect is that you wind up with a much better proportioned working space.
Try it – in particular, if you’ve got a netbook computer that has a 1024x600 display, you’ll immediately appreciate the extra space for browsing the Internet. For the first day you’ll feel a little out of sync, but then I guarantee you’ll become an enthusiastic convert!
15. Pin Your Favorite Folders. If you’re always working in the same four or five folders, you can quickly pin them with the Explorer icon on the taskbar. Hold the right-click button down and drag the folder to the taskbar, and it will be automatically pinned in the Explorer Jump List.
16. Starting Explorer from “My Computer”. If you spend more time manipulating files outside of the documents folders than inside, you might want to change the default starting directory for Windows Explorer so that it opens at the Computer node:
To do this, navigate to Windows Explorer in the Start Menu (it’s in the Accessories folder). Then edit the properties and change the target to read:
%SystemRoot%\explorer.exe /root,::{20D04FE0-3AEA-1069-A2D8-08002B30309D}
If you want the change to affect the icon on the taskbar, you’ll need to unpin and repin it to the taskbar so that the new shortcut takes effect. It’s worth noting that Win+E will continue to display the documents library as the default view: I’ve not found a way to change this from the shell at this time.
17. ClearType Text Tuning and Display Color Calibration. If you want to tune up your display for image or text display, we have the tools included out of the box. It’s amazing what a difference this makes: by slightly darkening the color of the text and adjusting the gamma back a little, my laptop display looks much crisper than it did before. You’d adjust the brightness and contrast settings on that fancy 42” HDTV you’ve just bought: why wouldn’t you do the same for the computer displays that you stare at every day? Check out cttune.exe and dccw.exe respectively, or run the applets from Control Panel.
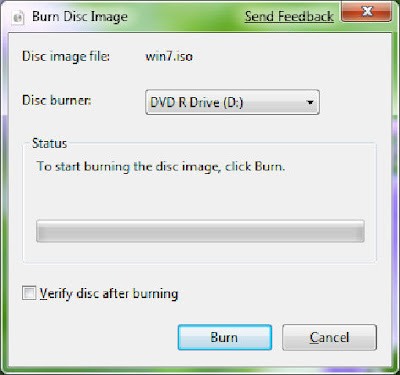
18. ISO Burning. Easy to miss if you’re not looking for it: you can double-click on any DVD or CD .ISO image and you’ll see a helpful little applet that will enable you to burn the image to a blank disc. No more grappling for shareware utilities of questionable parentage!
19. Windows Movie Maker. Windows 7 doesn’t include a movie editing tool – it’s been moved to the Windows Live Essentials package, along with Photo Gallery, Mail and Messenger. Unfortunately, Windows Live Movie Maker is currently still in an early beta that is missing most of the old feature set (we’re reworking the application), and so you might be feeling a little bereft of options. It goes without saying that we intend to have a better solution by the time we ship Windows 7, but in the meantime the best solution for us early adopters is to use Windows Movie Maker 2.6 (which is essentially the same as the most recent update to the Windows XP version). It’s missing the full set of effects and transitions from the Windows Vista version, and doesn’t support HD editing, but it’s pretty functional for the typical usage scenario of home movie editing.
Download Windows Movie Maker 2.6 from here:
http://microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=d6ba5972-328e-4df7-8f9d-068fc0f80cfc
20. Hiding the Windows Live Messenger Icon. Hopefully your first act after Windows 7 setup completed was to download and install the Windows Live Essentials suite of applications (if not, then you’re missing out on a significant part of the Windows experience). If you’re a heavy user of IM, you may love the way that Windows Live Messenger is front and central on the taskbar, where you can easily change status and quickly send an IM to someone:
On the other hand, you may prefer to keep Windows Live Messenger in the system tray where it’s been for previous releases. If so, you can fool the application into the old style of behavior. To do this, close Windows Live Messenger, edit the shortcut properties and set the application to run in Windows Vista compatibility mode. Bingo!

______________